Author: xdsystem
Production Process
Below is the scheme of the ship prototype production process
Ship frame assembly

![]() Laying of the ship’s shell
Laying of the ship’s shell

![]() Applying polyester membrane and resin to the shell
Applying polyester membrane and resin to the shell

![]() Putty coating on the shell
Putty coating on the shell

![]() Component installation
Component installation

![]() and ship trial.
and ship trial.

Electrical Components
In the operation of this fast patrol boat is a combination of the work of several electrical components that are integrated with each other, including: RadioLink 4ch Digital RCBS with a 2.4 GHz frequency remote control, receiver, 120 Amp ESC, 20 kg of power and DC current 4.8 ~ 6.8 v servo, 2200 kv motor, and Lipo 3 cell (11.1 v) 5500 mAh battery.
Remote Control
Receiver and ESC

Servo

Motor

Battery

Materials
Selection of the right material is needed in the construction of the ship prototype. The materials used are: 3mm plywood, 2mm balsa wood, polyester membrane, polyester putty, and resin.
3mm Plywood
2mm Balsa Wood

Polyester Membrane
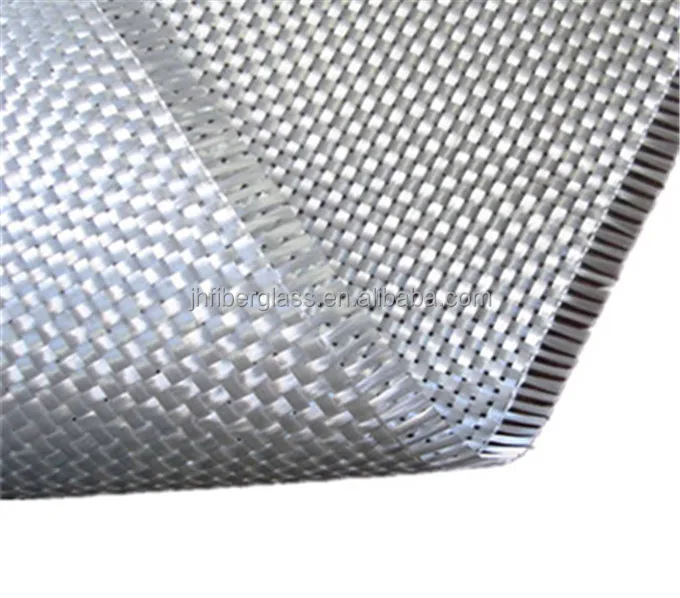
Polyester Putty

Resin

Wave Elevation
The software used for wave elevation simulation uses the Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) Tdyn software version 14.0.1. The numerical simulation process begins with the making of a ship model in .Iges format that can be obtained by exporting the “Development Design” file’s from Rhinoceros 5.0. Then the next step is the making of a boundary layer and meshing boundary. CFD simulations on this fast patrol boat are specifically for seeing ship wave elevation against fluids as shown below
Wave Elevation
Meshing Boundary

Resistance Analysis
Analysis of ship resistance is carried out using the maxsurf software with Savitsky and Slender Body method as shown in the graph below.

Seakeeping Analysis
By entering the radius of gyration value from the results of the previous post calculations, then seakeeping analysis is carried out with a speed criteria of 30 knots, heading angle 180°, and adding the Bretschneider or ITTC wave spectrum criteria to the maxsurf software, the results of seakeeping analysis in RAO graph generated as in the picture below

Radius of Gyration
Ship motion prediction programs such as maxsurf require a ship’s radius of gyration (or gyradius) around the longitudinal, transverse, and vertical axes passing through its center of gravity. The gyradius is defined as the square root of the ratio of total rotational inertia to mass for each axis:
 xi= longitudinal origin distance to center of gravity
xi= longitudinal origin distance to center of gravity
yi= transverse distance origin to center of gravity
zi= vertical distance from origin to center of gravity
wi= mass of each element (section)
Calculation table:

So the calculation becomes as follows:

The value results calculated above will be used in the next post session.
Curve of Sectional Area
Curve of sectional area (CSA) is a curve that shows the area of the ship at each station as shown below

Hydrostatic Analysis
In order to ease the hydrostatic analysis process, this ship’s design was enlarged 30 times. Comparison of dimensions, wetted surface area (WSA), volume, and displacement between scaled ships and ship prototypes are listed in the table below. The principal dimension scale does not apply to all quantities. To calculate other variables such as speed and force, we use the comparison formula of the scale factor based on Froude’s law about the similarity of geometric, kinematic and dynamic aspects in both objects.

Then, the scaled model was imported in the maxsurf software to analyze its hydrostatic properties. the ship’s model and the results of the hydrostatic calculation are in the picture below


